
The forex market represents the world’s largest financial playground, where $7.5 trillion changes hands daily through currency exchanges. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or curious beginner, understanding this dynamic marketplace opens doors to unprecedented profit opportunities. This comprehensive guide unveils everything from basic currency pairs to advanced trading strategies, empowering you to navigate the forex landscape with confidence and precision.
Key Takeaways
- Market Scale Matters: The forex market’s $7.5 trillion daily volume dwarfs all other financial markets combined, offering unparalleled liquidity and trading opportunities around the clock.
- Currency Pairs Rule Everything: Success hinges on understanding how major, minor, and exotic currency pairs behave, with EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY dominating 70% of all trades.
- Leverage is a Double-Edged Sword: While 100:1 leverage can amplify profits dramatically, proper risk management and understanding margin requirements separate profitable traders from blown accounts.
- Multiple Trading Styles Exist: From scalpers capturing pip movements in minutes to position traders holding for months, finding your natural trading rhythm is crucial for long-term success.
- Technology and Psychology Intertwine: Modern forex trading combines sophisticated platforms with emotional discipline, where technical analysis meets mental fortitude in the pursuit of consistent profits.
Introduction
Picture this: while you’re sipping your morning coffee, traders in Tokyo are already deep into their lunch break, London markets are buzzing with midday activity, and somewhere in Sydney, the trading day is winding down. This is the beauty of the forex market – it never sleeps, never stops, and never fails to surprise even the most experienced traders.
I’ve spent years watching traders transform from complete novices to market masters, and I can tell you this: the forex market isn’t just about numbers on a screen. It’s about understanding global economics, reading between the lines of central bank policies, and sometimes, trusting your gut when technical analysis meets real-world chaos.
The foreign exchange market, or forex as we affectionately call it, stands as the ultimate testament to global interconnectedness. Every political decision, every economic announcement, every natural disaster ripples through this vast ocean of currencies, creating waves of opportunity for those who know how to surf them.
What is the Forex Market?
Let me paint you a picture. Imagine the largest bazaar in the world, where instead of spices and textiles, people trade currencies. That’s essentially what the forex market is – a global decentralized marketplace where currencies are bought and sold 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Unlike the stock market with its physical locations and opening bells, the forex market exists in cyberspace, connecting banks, corporations, governments, and individual traders across continents. It’s like a massive digital web where every transaction, no matter how small, contributes to the constant fluctuation of exchange rates.
The forex market operates through a network of banks, brokers, and financial institutions rather than a centralized exchange. This decentralized nature means that trading happens simultaneously across major financial centers: London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. When one market closes, another opens, creating a seamless 24-hour trading cycle that never truly stops.
What makes this market truly fascinating is its sheer scale. According to the Bank for International Settlements, the average daily trading volume exceeds $7.5 trillion. To put that in perspective, that’s more than the GDP of most countries – traded every single day!
Forex vs Stock Market: The Ultimate Showdown
Here’s where things get interesting, and I often get asked this question: “Should I trade forex or stocks?” Well, let me break it down for you.
| Aspect | Forex Market | Stock Market |
|---|---|---|
| Trading Hours | 24/5 continuous | Limited to exchange hours |
| Market Size | $7.5 trillion daily | $200 billion daily |
| Leverage | Up to 500:1 | Typically 2:1 |
| Number of Options | ~30 major pairs | Thousands of stocks |
| Volatility | Moderate to high | Varies by stock |
| Entry Barrier | Low ($100+) | Moderate ($500+) |
The forex market offers something the stock market simply can’t match: pure liquidity. When you want to exit a position, you can almost always find a buyer or seller. Try doing that with a penny stock at 3 AM!
But here’s the kicker – the stock market offers ownership in actual companies. When you buy Apple stock, you own a tiny piece of Apple. In forex, you’re essentially betting on one country’s economic performance against another’s. Both have their charm, but forex trading offers more flexibility and accessibility for most retail traders.

Understanding Currency Pairs: The Building Blocks of Forex
Think of currency pairs as the DNA of forex trading. Every trade involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. It’s like a financial tango where two currencies dance together, their relationship determining your profit or loss.
Major Currency Pairs: The Heavy Hitters
The major pairs are the celebrities of the forex world. They include:
- EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) – The world’s most traded pair
- GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar) – Known as “Cable”
- USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen) – The Asian powerhouse
- USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc) – The safe haven play
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar) – The commodity currency
- USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar) – The neighbor’s pair
- NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar/US Dollar) – The Kiwi
These pairs represent about 70% of all forex trading volume. Why? Because they involve the world’s most stable and liquid currencies, backed by robust economies and transparent monetary policies.
Minor and Exotic Pairs: The Wild Cards
Minor pairs don’t include the US Dollar but feature other major currencies like EUR/GBP or GBP/JPY. They’re like the supporting actors – important but with less spotlight and typically wider spreads.
Exotic pairs? These are the rebels of forex trading. Think USD/TRY (Turkish Lira) or EUR/ZAR (South African Rand). They can be wildly profitable but equally dangerous due to their volatility and lower liquidity.
The Mechanics: Bid, Ask, Spread, and All That Jazz
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how forex trading actually works. Understanding these concepts isn’t just important – it’s essential for your survival in this market.
Bid and Ask: The Eternal Dance
The bid is what buyers are willing to pay for a currency, while the ask is what sellers are demanding. The difference between these two prices is called the spread, and it’s essentially the cost of doing business in forex.
Imagine you’re at a car dealership. The sticker price is the “ask,” but you know you can negotiate. Your opening offer is the “bid.” The final agreed price is somewhere in between – that’s essentially how forex pricing works, except it happens millions of times per second.
Pips: The Smallest Move That Matters
A pip (percentage in point) is typically the fourth decimal place in a currency quote. For most pairs, one pip equals 0.0001. So if EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1001, that’s a one-pip movement.
Here’s something most beginners don’t realize: pip values change based on your position size and the currency pair you’re trading. For a standard lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD, one pip is worth $10. But for USD/JPY, which quotes to two decimal places, one pip (0.01) might be worth about $9.10, depending on the current exchange rate.
Lots and Leverage: Size Matters
A lot is the standard unit size for trading. A standard lot is 100,000 units of the base currency. Mini lots are 10,000 units, and micro lots are 1,000 units. Most retail brokers now offer nano lots of 100 units, making forex accessible to traders with smaller accounts.
Leverage is where forex gets really interesting – and dangerous. It allows you to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. With 100:1 leverage, you can control $100,000 worth of currency with just $1,000 in your account.
But remember: leverage magnifies both profits and losses. I’ve seen traders double their accounts in a day, and I’ve seen others lose everything just as quickly. Leverage is a tool, not a toy.
How Currency Pairs Work in the Forex Market
Understanding how currency pairs function is like learning the grammar of a new language. Once you get it, everything else starts making sense.
When you see EUR/USD quoted at 1.1000, it means one Euro is worth 1.10 US Dollars. The first currency (EUR) is called the “base currency,” and the second (USD) is the “quote currency.” If you think the Euro will strengthen against the Dollar, you buy EUR/USD. If you think it will weaken, you sell it.
The Correlation Game
Currency pairs don’t exist in isolation. They’re connected through complex relationships that can work for or against you. For example:
- Positive Correlation: EUR/USD and GBP/USD often move in the same direction
- Negative Correlation: USD/CHF typically moves opposite to EUR/USD
- Commodity Correlation: AUD/USD often follows gold prices
Understanding these relationships helps you avoid overexposure to similar risks and can provide trading opportunities when correlations break down.

Earning Through Strategic Forex Trading
Let’s talk money – specifically, how to make it in forex without losing your shirt in the process.
The Foundation: Risk Management
Before discussing profit strategies, let me share something crucial: successful forex trading is more about not losing money than making money. Sounds counterintuitive? Let me explain.
If you lose 50% of your account, you need a 100% return just to break even. Lose 75%, and you need a 300% return. The math gets ugly fast, which is why protecting your capital is paramount.
Position Sizing Rules:
- Never risk more than 2% of your account on a single trade
- Use stop losses on every position
- Calculate your position size before entering any trade
Strategic Approaches to Profit
1. Trend Following The old adage “the trend is your friend” exists for good reason. Trends can persist longer than logic suggests, and riding them can be incredibly profitable.
2. Range Trading When markets aren’t trending, they’re often ranging – bouncing between support and resistance levels. Range traders buy at support and sell at resistance, profiting from predictable price action.
3. Breakout Trading Sometimes, prices break out of established ranges or patterns, leading to significant moves. Breakout traders position themselves to catch these momentum shifts.
4. News Trading Economic announcements can cause dramatic price movements. News traders position themselves around these events, though this approach requires quick reflexes and strong risk management.
Buy vs Sell Positions: The Art of Direction
In forex, every trade is essentially a bet on which way a currency pair will move. But here’s where it gets interesting – you can profit whether prices go up or down.
Buy Positions (Going Long)
When you buy a currency pair, you’re purchasing the base currency and selling the quote currency. You profit if the base currency strengthens relative to the quote currency.
Example: You buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, believing the Euro will strengthen. If it rises to 1.1050, you’ve made 50 pips profit.
Sell Positions (Going Short)
Selling a currency pair means you’re selling the base currency and buying the quote currency. You profit if the base currency weakens relative to the quote currency.
Example: You sell GBP/USD at 1.3000, believing the Pound will weaken. If it drops to 1.2950, you’ve made 50 pips profit.
The beauty of forex is this flexibility – you can profit in any market condition if you correctly predict direction.
Essential Skills for Forex Beginners
Starting your forex journey without proper preparation is like sailing into a storm without a compass. Here are the fundamental skills every beginner needs:
Technical Analysis Mastery
Chart Reading: Understanding candlestick patterns, support and resistance levels, and trend lines forms the foundation of technical analysis.
Indicator Usage: Learn to use moving averages, RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands effectively. But remember – indicators are tools, not crystal balls.
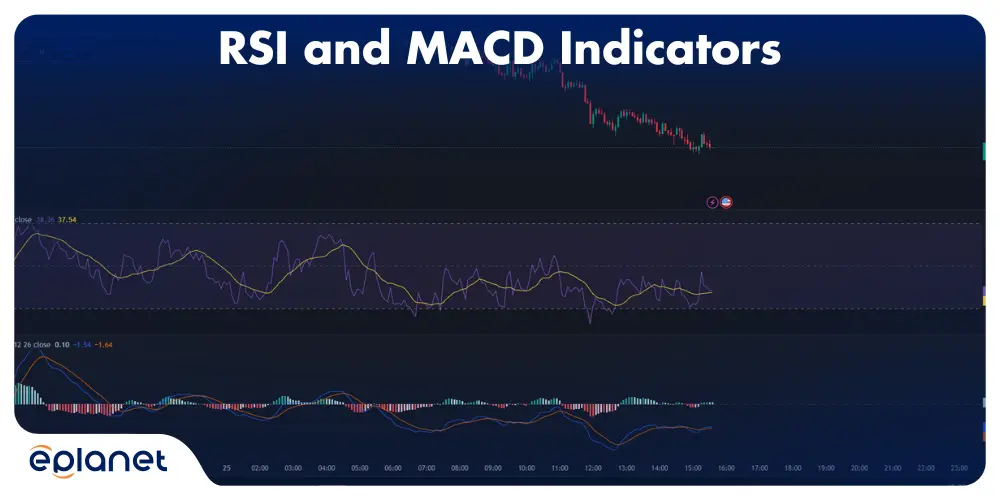
Fundamental Analysis Understanding
Currency values are ultimately driven by economic fundamentals:
- Interest Rates: Higher rates typically attract foreign investment
- Economic Growth: Strong GDP growth usually supports currency strength
- Political Stability: Uncertainty can cause currency volatility
- Trade Balance: Countries with trade surpluses often have stronger currencies
Risk Management Discipline
This might be the most important skill of all. Develop ironclad rules for:
- Maximum risk per trade
- Daily loss limits
- Position sizing calculations
- Stop loss placement
Emotional Control
Forex trading is as much a psychological game as it is technical. Develop strategies to handle:
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Revenge trading after losses
- Overconfidence after wins
- Analysis paralysis
Types of Traders: Finding Your Trading Personality
Not all traders are created equal, and that’s perfectly fine. The key is finding a trading style that matches your personality, schedule, and risk tolerance.
Scalpers: The Speed Demons
Scalpers are the adrenaline junkies of forex trading. They hold positions for seconds to minutes, aiming to capture small price movements multiple times throughout the day.
Characteristics:
- Hold positions for 1-15 minutes
- Target 5-10 pips per trade
- Make 50-200 trades per day
- Require intense focus and quick decision-making
Pros: Quick profits, limited overnight risk.
Cons: High stress, significant time commitment, large spreads eat into profits.
Day Traders: The Balanced Approach
Day traders close all positions before the market closes, avoiding overnight risk while still capitalizing on intraday price movements.
Characteristics:
- Hold positions for minutes to hours
- Target 10-100 pips per trade
- Make 1-10 trades per day
- Balance analysis with execution
Many day traders rely on the 5-minute EMA as their go-to indicator for trend identification and dynamic support/resistance. When price stays above the 5-minute EMA, they focus on long opportunities, and when below, they hunt for short setups. This simple tool helps day traders stay aligned with short-term momentum while filtering out choppy, sideways markets that can eat into profits.
Pros: No overnight risk, good profit potential, manageable time commitment.
Cons: Requires market monitoring during trading hours.
Swing Traders: The Patient Hunters
Swing traders capture larger price movements over several days to weeks, riding the natural ebb and flow of market sentiment.
Characteristics:
- Hold positions for days to weeks
- Target 50-500 pips per trade
- Make 1-10 trades per week
- Focus on technical and fundamental analysis
Pros: Less time-intensive, larger profit potential, suits working professionals.
Cons: Overnight and weekend risk, requires patience.
Position Traders: The Long-Term Visionaries
Position traders are the marathon runners of forex, holding positions for weeks to months based on long-term economic trends.
Characteristics:
- Hold positions for weeks to months
- Target 200-2000+ pips per trade
- Make 1-5 trades per month
- Focus heavily on fundamental analysis
Pros: Minimal time commitment, massive profit potential, less stress.
Cons: Requires significant capital, long drawdown periods, substantial overnight risk.
Advanced Concepts: Taking Your Trading to the Next Level
Market Makers vs ECN Brokers
Understanding your broker type affects your trading experience significantly:
Market Makers create their own prices and may trade against you. They often offer fixed spreads and no commission but might have conflicts of interest.
ECN (Electronic Communication Network) Brokers connect you directly to the interbank market, offering variable spreads and charging commissions but providing more transparent pricing.
Swap Rates and Carry Trading
Swap rates are the interest rate differentials between currency pairs. If you hold a position overnight, you either pay or receive interest based on these differentials.
Carry trading involves buying currencies with high interest rates and selling those with low rates, profiting from the interest differential over time. It’s like getting paid to hold a position, but currency movements can quickly wipe out interest gains.
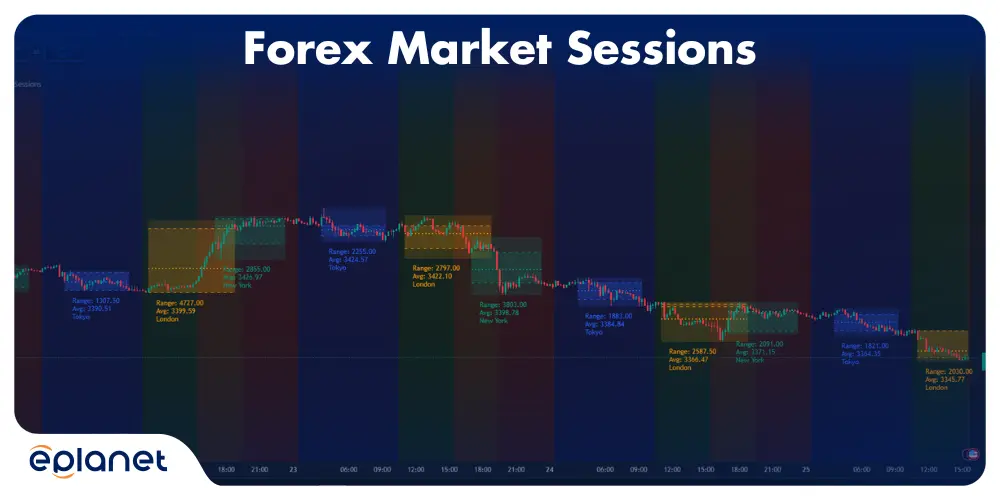
Liquidity and Market Hours
Liquidity varies throughout the trading day. The most liquid periods occur when major sessions overlap:
- London-New York Overlap (8 AM – 12 PM EST): Highest volume and tightest spreads
- Asian-London Overlap (3 AM – 4 AM EST): Moderate activity
- Sydney-Tokyo Overlap (7 PM – 2 AM EST): Lower but consistent activity
Understanding Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
Let me share something that separates winning traders from the rest: they always know their exit strategy before entering a trade.
Stop Loss: Your Financial Safety Net
A stop loss is an order that automatically closes your position when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. It’s not optional – it’s essential.
Types of Stop Losses:
- Fixed Pips: Set a specific number of pips from entry
- Percentage: Risk a fixed percentage of account balance
- Technical: Place stops beyond support/resistance levels
- Trailing: Automatically adjust as price moves in your favor
Take Profit: Locking in Success
A take profit order automatically closes your position when you’ve achieved your target profit. While not mandatory like stop losses, they help remove emotion from profit-taking decisions.
Take Profit Strategies:
- Risk-Reward Ratios: Target 2:1 or 3:1 reward-to-risk ratios
- Technical Levels: Exit at resistance/support levels
- Partial Profits: Close portions of positions at different levels
The Psychology Behind Orders
Here’s something most trading courses won’t tell you: the hardest part about stop losses and take profits isn’t setting them – it’s sticking to them. I’ve watched countless traders move their stop losses further away when trades go against them, turning small losses into account killers.
CFD Trading: Expanding Your Horizons
Contract for Difference (CFD) trading allows you to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset. While primarily associated with stocks and commodities, CFDs play an important role in modern forex trading platforms.
CFD Advantages:
- Access to global markets from one platform
- Ability to go long or short easily
- Leverage availability across multiple asset classes
- No stamp duty in many jurisdictions
CFD Considerations:
- Overnight financing costs
- Counterparty risk with broker
- No ownership rights
- Potential for significant losses
Many forex brokers now offer CFDs on indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies alongside currency pairs, allowing traders to diversify their strategies across multiple markets.
Risk Management: Your Trading Lifeline
Let me be brutally honest: most traders fail not because they can’t identify good trades, but because they don’t manage risk properly. Risk management isn’t glamorous, but it’s what separates professionals from gamblers.
The 2% Rule
Never risk more than 2% of your trading account on any single trade. This rule ensures that even with a string of losses, you’ll still have capital to trade another day.
Example Calculation:
- Account Size: $10,000
- Maximum Risk: $200 (2%)
- If stop loss is 50 pips, position size should be 4 micro lots
Diversification Strategies
Don’t put all your eggs in one currency basket:
- Trade different currency pairs
- Use various timeframes
- Employ multiple trading strategies
- Avoid correlated positions
Smart Money Concepts: Following the Big Players
Smart money concepts revolutionize risk management by teaching you to think like institutional traders. Instead of placing stops at obvious technical levels, order flow analysis helps you identify where large players accumulate positions, allowing smarter stop placement. Liquidity hunting shows how institutions target retail stop clusters, helping you avoid these traps. Understanding market structure lets you align with higher timeframe flows for better risk-reward ratios. Smart money doesn’t just ask “Will this trade profit?” but “How does this fit our overall risk profile?” – thinking that transforms individual trades into portfolio management.
The Kelly Criterion
For advanced traders, the Kelly Criterion can help optimize position sizing based on win rate and average win/loss ratio:
Kelly % = (Win Rate × Average Win) / Average Loss – (1 – Win Rate)
While mathematically sound, the Kelly Criterion often suggests position sizes that are too aggressive for most traders’ comfort levels.
Technology and Tools: Your Trading Arsenal
Modern forex trading relies heavily on technology. Your success often depends on having the right tools and knowing how to use them effectively.
Trading Platforms
MetaTrader 4/5: The industry standard for retail forex trading
- Extensive charting capabilities
- Custom indicator support
- Automated trading options
- Mobile accessibility
cTrader: Growing in popularity for its intuitive interface
- Advanced order types
- Level II pricing
- Better execution transparency
Proprietary Platforms: Many brokers offer custom platforms
- Often tailored to specific trading styles
- May offer unique features
- Usually web-based for accessibility
Essential Tools
Economic Calendars: Track high-impact news events.
Position Size Calculators: Ensure proper risk management.
Correlation Matrices: Understand pair relationships.
Pivot Point Calculators: Identify potential support/resistance levels.
Mobile Trading
The ability to monitor and adjust positions on the go has revolutionized forex trading. However, mobile trading should complement, not replace, your primary analysis platform.
The Psychology of Forex Trading
Here’s what nobody tells you about forex trading: your biggest enemy isn’t the market – it’s yourself. The psychological aspects of trading often determine success more than technical knowledge.
Common Psychological Traps
Overconfidence: A few winning trades can lead to excessive risk-taking.
Revenge Trading: Trying to quickly recover losses often leads to bigger losses.
Analysis Paralysis: Over-analyzing trades until opportunities pass.
FOMO: Fear of missing out leads to chasing trades and poor entries.
Developing Mental Discipline
Keep a Trading Journal: Document not just what you traded, but why and how you felt.
Stick to Your Plan: Develop a trading plan and follow it religiously.
Accept Losses: Losses are part of trading; the goal is to keep them small.
Celebrate Small Wins: Acknowledge progress and successful execution.
Stress Management
Forex trading can be incredibly stressful. Develop healthy coping mechanisms:
- Regular exercise
- Adequate sleep
- Proper nutrition
- Breaks from trading
- Meditation or mindfulness practices
Building Your Forex Trading Plan
A trading plan is your roadmap to consistent profitability. Without one, you’re essentially gambling with good odds.
Plan Components
Trading Goals form the foundation of any successful trading plan. You need to establish realistic return expectations that align with your skill level and market conditions. Consider what maximum acceptable losses you can handle both financially and emotionally, while honestly assessing the time commitment you can dedicate to trading activities.
Risk Management Rules represent the most critical aspect of your plan. Define your maximum risk per trade, typically no more than 2% of your account balance. Establish clear daily and weekly loss limits that force you to step away when emotions might cloud your judgment. Develop consistent position sizing methods that automatically calculate appropriate trade sizes based on your risk parameters.
Trading Strategy encompasses the tactical elements of your approach. Your entry criteria should be specific and measurable, removing guesswork from when to enter positions. Similarly, your exit criteria need to be predetermined, covering both profit-taking and loss-cutting scenarios. Choose specific time frames that match your lifestyle and personality, whether that’s scalping on minute charts or swing trading on daily charts. Focus on particular currency pairs rather than trying to trade everything, allowing you to develop expertise in their unique characteristics.
Performance Metrics help you measure success objectively. Set realistic win rate expectations based on your strategy type, understanding that some approaches might win only 40% of the time while still being profitable. Target specific average risk-reward ratios that ensure your winning trades more than compensate for your losses. Finally, determine your maximum drawdown tolerance, knowing the largest percentage decline you can psychologically and financially withstand.
Plan Implementation
Start Small: Begin with micro lots and minimal risk.
Track Everything: Maintain detailed records of all trades.
Review Regularly: Analyze performance weekly/monthly.
Adapt Carefully: Make gradual improvements based on data.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning from others’ mistakes is cheaper than learning from your own. Here are the most common forex trading errors I’ve witnessed:
Overleverage
Mistake: Using excessive leverage (200:1, 400:1) for quick profits.
Reality: High leverage leads to quick account destruction.
Solution: Start with 10:1 or 20:1 leverage maximum.
No Stop Losses
Mistake: Trading without stop losses, hoping losing trades will recover.
Reality: Small losses become account killers.
Solution: Always use stop losses, no exceptions.
Emotional Trading
Mistake: Making decisions based on fear, greed, or revenge.
Reality: Emotions lead to poor trading decisions.
Solution: Develop and follow a mechanical trading system.
Inadequate Education
Mistake: Starting with real money before understanding the basics.
Reality: Forex is complex and requires significant learning.
Solution: Use demo accounts extensively before going live.
Chasing Hot Tips
Mistake: Following “guaranteed” trading signals or hot tips.
Reality: No one can predict the market with certainty.
Solution: Develop your own analysis skills and trust your judgment.
The Future of Forex Trading
The forex market continues evolving with technological advances and changing global economics. Several trends are shaping its future:
Algorithmic Trading
High-frequency trading and algorithmic systems now dominate the institutional forex market. While retail traders can’t compete on speed, understanding algorithmic behavior can provide trading opportunities.
Cryptocurrency Integration
Digital currencies are increasingly affecting traditional forex markets. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies often move inversely to traditional safe-haven currencies during times of uncertainty.
Artificial Intelligence
AI-powered analysis tools are becoming more sophisticated and accessible to retail traders. However, human judgment and emotional control remain irreplaceable.
Regulatory Changes
Increasing regulation in major markets is affecting leverage limits, broker operations, and trader protections. Stay informed about regulatory changes in your jurisdiction.

Conclusion
The forex market offers unparalleled opportunities for those willing to approach it with respect, discipline, and continuous learning. It’s not a get-rich-quick scheme, nor is it an impossible puzzle reserved for financial geniuses. It’s a skill-based endeavor that rewards patience, discipline, and smart risk management.
Remember these key points as you begin or continue your forex journey:
Success in forex trading comes from mastering the fundamentals, developing discipline, and maintaining realistic expectations. The market will always be there, but your capital won’t if you don’t protect it properly.
Start small, learn continuously, and never risk money you can’t afford to lose. The traders who succeed are those who view forex as a marathon, not a sprint. They understand that consistent small profits compound over time into significant wealth.
Your forex education doesn’t end with this article – it’s just beginning. The market will teach you lessons that no book or course can. Embrace those lessons, learn from your mistakes, and never stop improving your skills.
The forex market awaits, but are you ready for it? Take your time, prepare thoroughly, and when you do take that first live trade, make sure you’re doing it with a plan, proper risk management, and realistic expectations.
Ready to start your forex journey? Begin with a demo account, practice these concepts, and remember – every expert was once a beginner. The question isn’t whether you can succeed in forex trading; it’s whether you’re willing to put in the work required to succeed.
For more comprehensive information about forex trading mechanics and getting started, check out this detailed resource from Bank of America’s guide to forex trading.
What’s your next move in the forex market going to be?
Disclaimer: Forex trading involves substantial risk and is not suitable for all investors. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making investment decisions.

